Description
The management of a logistics warehouse is a complex challenge that requires precision and strategy. The rise of e-commerce has revolutionized traditional distribution methods, prompting businesses to optimize every facet of their distribution centers. This article explores ten critical aspects of warehouse management, highlighting best practices for increased efficiency.
1. Infrastructure and Equipment
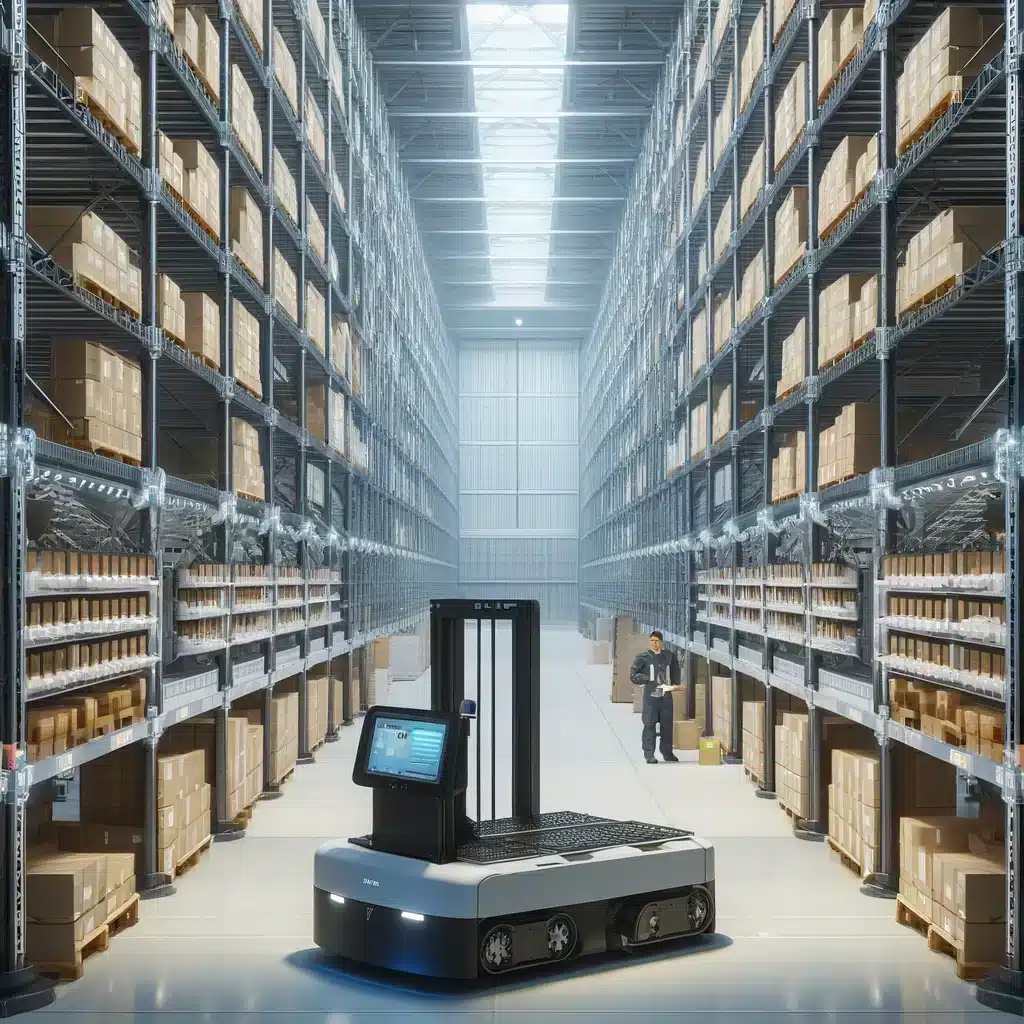
The infrastructure of the warehouse must promote the smooth flow of goods. The use of cutting-edge equipment, such as automated storage and retrieval systems, can significantly increase productivity.
The layout of a warehouse requires strategic design to optimize every square meter. Infrastructures must support modern handling equipment that allows for the easy movement of goods. Wide aisles, dedicated storage areas, and ergonomic workspaces are essential elements. Solutions such as high-density shelving and vertical storage systems take advantage of the warehouse’s height, thus increasing storage capacity without compromising the speed of access to goods.
In a world where speed is synonymous with competitiveness, advanced equipment is the cornerstone of effective warehouse management. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), integrated with intelligent inventory management software, reduce human error and speed up operations. Automated conveyors, laser-guided forklifts, and order picking robots are all investments that result in increased efficiency and better profitability.
A modern warehouse must remain agile, capable of adapting to technological evolutions. It is essential to plan for scalable infrastructures that can accommodate new automation or robotics solutions. Furthermore, the preventative maintenance of equipment is fundamental to avoid unexpected interruptions that could slow down or halt production. A regular maintenance program ensures not only the longevity of equipment but also the safety of operators, an aspect never to be overlooked in the day-to-day management of the warehouse.
2. Inventory Management Systems
An effective inventory management system is crucial. The adoption of intelligent software solutions provides real-time visibility and reduces the risk of error.
An effective inventory management system is the cornerstone of a high-performing warehouse, maintaining the delicate balance between sufficient supply and costly stock excess. Modern software solutions play a vital role in this orchestration, providing unprecedented visibility over every item at every process stage. These systems meticulously record the entry and exit of goods, monitor stock levels in real time, and automatically alert when levels approach critical thresholds. By incorporating artificial intelligence, they predict trends and adjust orders, thus ensuring a dynamic response to fluctuating demand. Therefore, an efficient inventory management system is not just a tracking tool but a genuine strategic partner in the optimization of stock flow.
Stock errors are not only costly but can also damage a company’s reputation. Intelligent software solutions minimize this risk by automating tasks such as data entry, replenishment, and inventory audits. Features such as barcode scanning or RFID technology simplify the process of registering and tracking products, reducing the time needed for physical inventories while increasing data accuracy. Employees, freed from repetitive and error-prone tasks, can focus on value-added operations. The advanced analytics provided by these systems also offer insights to eliminate bottlenecks, reduce downtime, and improve the flow of stocks, leading to a significant increase in overall productivity.
In a rapidly changing commercial environment, flexibility and scalability are indispensable features for inventory management systems. A system’s ability to adapt to variable volumes, incorporate new product categories, and connect with other enterprise systems (such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)) is fundamental. A good inventory management system can evolve with the company, adapt to technological innovations, and integrate smoothly with business processes. Additionally, the use of cloud data and collaborative platforms allows for real-time synchronization between different sites and departments, ensuring information consistency and transparency across the entire company. This interconnectivity accelerates informed decision-making and enables an agile response to market contingencies.
3. Receiving Processes
Receiving operations must be quick and error-free. The use of barcodes and RFID scanners ensures precise data entry into the system.
4. Storage and Organization
A rational organization of storage spaces is essential. The use of modular shelving systems optimizes space and access to products.
5. Shipment Management
Shipments must be managed with military precision. Carefully planning delivery routes can reduce delays and costs.
6. Safety and Compliance
Safety is paramount. Implementing strict protocols and following safety standards minimize the risks of accidents and losses.
7. Maintenance and Cleaning
A regular maintenance program ensures the proper functioning of equipment. Cleaning must be continuous to ensure an optimal working environment.
8. Training and Development of Personnel
Staff must be regularly trained to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and methods. Workshops and certification programs can enhance the team’s skills.
9. Data Analysis and Reporting
Data analysis helps identify trends and areas for improvement. The implementation of dynamic dashboards provides key information for decision-making.
10. Sustainable and Ecological Development
Integrating sustainable practices is both ethical and economical. Investing in eco-friendly solutions strengthens brand image and can lead to long-term savings.
Mastering the management of a warehouse in the dynamic context of modern commerce demands a thoughtful and technological approach. By incorporating these practices, distribution centers can turn logistical challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation.